
August 16, 2021
Overview
Clinical handover is defined as ‘the transfer of professional responsibility and accountability for some or all aspects of care for a patient or a group of patients, to another person or professional group on a temporary or permanent basis’.
Handover applies when transitions of care occur. A standardised approach to clinical handover facilitates effective and efficient communication, providing all staff with clear expectations and responsibilities for the ongoing care of the patient. This minimises risk to the patient.
Alignment to Western Health Best Care Framework
Safe Care & Coordinated Care
NSQHS Standard
Communicating for Safety
Why is this important?
A structured effective policy driven Clinical Handover is an essential tool to ensure patient safety. This can reduce the risk of incorrect/inappropriate treatment, delays to diagnosis and increasing length of stay.
Effective communication with a structure clinical handover tool ensures:
- Patient safety
- Appropriate care and treatment
- Structured and identifiable
- Accountability
- Patient engagement
What does this look like in practice?
Handover should occur between each transference of care, i.e. change of location, change of shift.
- All handovers should include the patient and, if available, family members and designated carers, allowing them to have an understanding of their treatment and care
- Both clinicians will undertake a three-point patient identification process at the bedside confirming full name, date of birth and patient identification number
- The identification and communication of all clinical alerts such as drug and food allergies, infection control precautions and modified MET Call and Code Blue criteria
- A review of the EMR to ensure medication administration and clinical orders have been completed.
- Handover should then be documented in the patient’s clinical notes using the handover sticker (Figure 1) and each nurse signs the bottom of the sticker
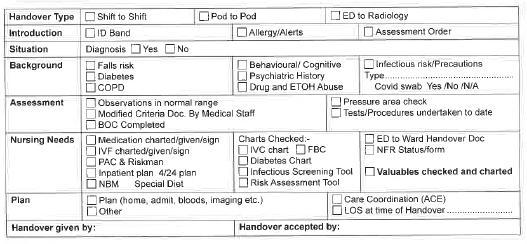
ED Shift Handover
Use of the ED handover sticker to guide and assist handover, minimising the potential for missed information.
- Involves direct patient handover occurring at the bedside. Between the nurses that currently holds the responsibility & the nurse who will be taking over the responsibility of care.
- Includes each patient & loved ones. Allowing them to have an understanding of their treatment & care.
- Both nurses will undertake a three-step patient identification process at the bedside confirming full name, date of birth & patient identification number.
- Identify all clinical alerts such as drug & food allergies, infection control precautions & modify MET call and code blue criteria.
- Once this is complete both nurses will need to undertake a review of EMR to ensure all medications & clinical orders have been attended to.
Handover should then be documented in the patient’s clinical notes using the handover sticker.
ED to Ward Handover
Phone handover utilising ISBAR format to confirmed unit to ANUM.
Utilising ISBAR form to communicate with receiving nurse.
ISBAR is essential to providing a consistent and concise systematic handover and should be used on every occasion.
Complete the following on EMR
- Ensure all medications are signed correctly on the MAR
- Record alerts, allergies, lines & devices
- COVID risk assessment completed
- Final set of vital signs
Performance
- Documentation Audit
- Riskman
- M&M
Policies, Procedures and Guidelines
Clinical Handover PPG
Patient Identification PPG
Hospital Transfer PPG
QRG’s
Clinical Handover QRG
- Please note the Clinical Handover QRG was recently update in June 2021
Communication Changes in the SHED QRG
External Links
Correct Clinical Handover Youtube Video
Australian Commission of Standard and Quality in Healthcare
Australian Nursing and Midwifery Journal – 5 Tips to a Good Clinical Handover
Webinar
News


